What is a Transformer? How It Works, Applications, and Safe Usage
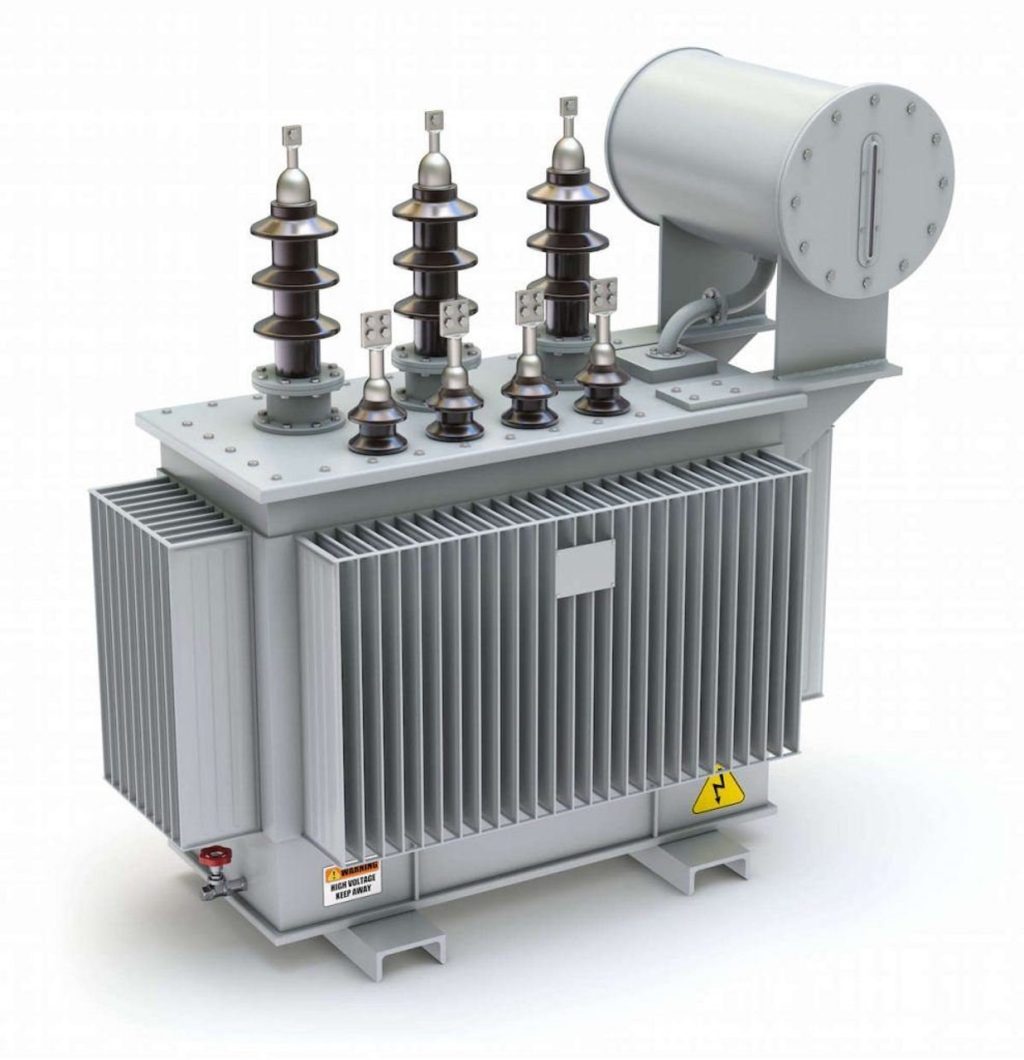

1. What is a Transformer?
A transformer is an electrical device designed to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. It is commonly used to increase (step-up) or decrease (step-down) voltage levels, making it essential for power distribution systems.
Types of Transformers:
- Step-up Transformer – Increases voltage from the primary to the secondary winding.
- Step-down Transformer – Decreases voltage from the primary to the secondary winding.
- Isolation Transformer – Provides electrical isolation between circuits without changing voltage levels.
- Autotransformer – Uses a single winding for both primary and secondary connections, offering variable voltage regulation.
- Toroidal Transformer – Designed in a circular shape, reducing electromagnetic interference.
Common Uses of Transformers:
- Power transmission and distribution
- Electrical appliances (e.g., chargers, televisions)
- Industrial machinery
- Medical equipment
2. How Does a Transformer Work?
The working principle of a transformer is based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. It consists of two main windings:
- Primary winding: Receives the input voltage.
- Secondary winding: Delivers the transformed voltage.
Both windings are wrapped around a magnetic core that enhances the efficiency of energy transfer. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it generates a magnetic field. This field induces an alternating voltage in the secondary winding, allowing electrical energy to transfer between circuits without direct electrical contact.
Key Components of a Transformer:
- Core – Typically made of laminated iron or ferrite to minimize energy loss.
- Windings – Coils of wire that carry current and create electromagnetic fields.
- Insulation – Ensures safety by preventing electrical leakage.
- Cooling System – Includes oil or air cooling to regulate temperature and prevent overheating.
3. Where Are Transformers Used?
Transformers play a crucial role in various industries and applications, including:
Power Transmission and Distribution
- Used by electrical utilities to step up voltage for transmission over long distances and step down voltage for safe residential and commercial use.
Industrial Applications
- Powering heavy machinery and equipment in manufacturing plants.
Household Appliances
- Found in devices like phone chargers, TVs, and microwave ovens to regulate voltage supply.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment
- Used in MRI machines, X-ray devices, and other sensitive electronic instruments requiring stable voltage levels.
Renewable Energy Systems
- Integrated into solar and wind power systems to convert generated electricity for grid compatibility.
4. How to Use a Transformer Safely?
While transformers are essential for electrical systems, improper handling can lead to hazards. Follow these safety precautions:
Installation Guidelines
- Ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical shocks.
- Keep transformers in well-ventilated areas to prevent overheating.
- Follow the manufacturer’s specifications for voltage and current ratings.
Operational Safety
- Never overload a transformer, as excessive current can cause overheating and failure.
- Regularly inspect for signs of wear, such as damaged insulation or loose connections.
- Keep transformers away from flammable materials to reduce fire risk.
Maintenance Tips
- Perform routine inspections and cleaning.
- Monitor temperature levels to prevent overheating.
- Replace worn-out or faulty components immediately to ensure safe operation.
Emergency Handling
- In case of smoke or unusual noise, disconnect power immediately.
- Avoid touching exposed wires or terminals.
- Contact a professional electrician for repairs.
Conclusion
Transformers are fundamental to modern electrical systems, providing efficient voltage regulation and energy transfer. Understanding how transformers work, where they are used, and how to handle them safely ensures optimal performance and longevity. Whether in industrial, household, or medical applications, proper usage and maintenance are key to safe and efficient transformer operation.