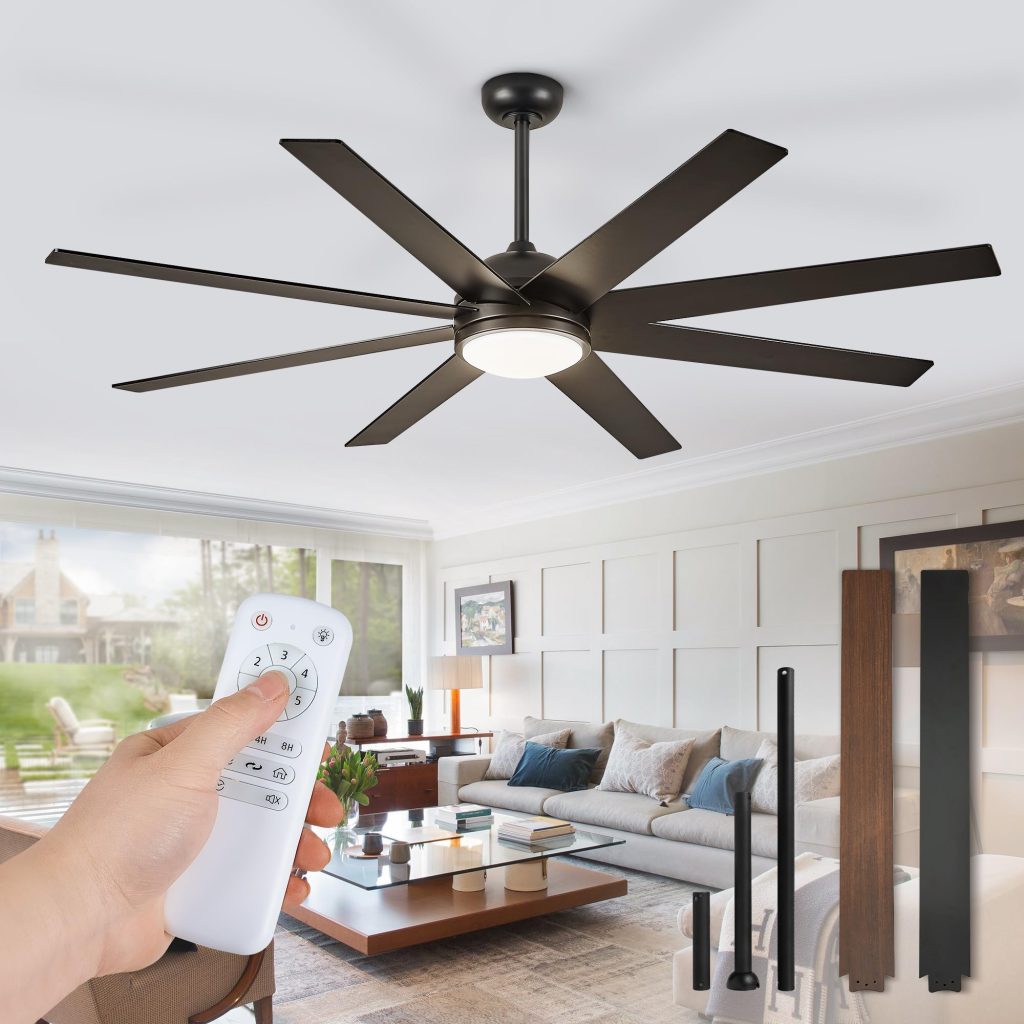
Ceiling Fans: What They Are, How They Work, Applications, and Safe Usage

Version 1.0.0
Ceiling fans are a popular and cost-effective way to circulate air, providing comfort and cooling in various environments. Whether in homes, offices, or other public spaces, ceiling fans help to create a pleasant atmosphere by improving air circulation. This article will cover the basic function of ceiling fans, how they work, their common applications, and important safety tips for using them.
1. What Are Ceiling Fans? (Introduction, Common Types, and Uses)
A ceiling fan is a mechanical fan mounted on the ceiling, designed to circulate air in a room or space. Unlike air conditioners, ceiling fans do not lower the temperature directly but create airflow that helps the body feel cooler by enhancing the evaporation of sweat. They are commonly used to improve air circulation, making indoor spaces more comfortable.
Common Types of Ceiling Fans:
- Standard Ceiling Fans: These are the most common type, with three to five blades and varying speeds to control airflow.
- Energy-Efficient Ceiling Fans: These fans are designed to consume less power while providing adequate air circulation, making them ideal for energy-conscious consumers.
- Smart Ceiling Fans: Equipped with smart features, these fans can be controlled via smartphones or voice assistants, allowing users to adjust speed and settings remotely.
- Dual Motor Ceiling Fans: These fans have two motors, allowing for independent control of the fan blades and light fixtures, offering greater flexibility and functionality.
- Industrial Ceiling Fans: Typically larger and more powerful, these fans are used in commercial and industrial spaces like warehouses or large factories.
Uses of Ceiling Fans:
- Improving Comfort: Ceiling fans circulate air to provide cooling in warmer weather, making rooms feel more comfortable without the need for an air conditioner.
- Enhancing Air Circulation: Ceiling fans are often used in spaces where air circulation is poor, helping to eliminate stale air and increase ventilation.
- Energy Saving: By creating airflow and making rooms feel cooler, ceiling fans allow users to reduce reliance on air conditioners, saving on energy bills.
- Lighting: Many ceiling fans come equipped with light fixtures, providing both lighting and air circulation in one unit.
2. How Do Ceiling Fans Work? (Principle of Operation and Key Components)
Ceiling fans operate by using rotating blades to move air throughout a room. The airflow they generate helps to circulate air, which can create a breeze that makes you feel cooler by enhancing heat dissipation from your body. The process is relatively simple but highly effective in improving comfort.
Key Components of Ceiling Fans:
- Blades: The blades are the main component that moves air. They are usually made from materials like plastic, wood, or metal and come in different shapes and sizes.
- Motor: The motor powers the rotation of the fan blades. It is typically located in the center of the fan assembly and controls the speed and direction of the blades.
- Control Mechanism: Ceiling fans are equipped with a control switch or remote control, which allows users to adjust the fan’s speed or switch between modes (forward/reverse).
- Light Fixture (optional): Many ceiling fans come with built-in light fixtures that can provide additional illumination to the room.
How It Works:
- Motor Activation: When the fan is switched on, the motor begins to rotate, causing the blades to spin.
- Air Circulation: As the blades spin, they push air downwards or upwards, depending on the rotation direction. This creates a breeze that circulates the air in the room.
- Temperature Regulation: The moving air can create a wind-chill effect, making people feel cooler. This is particularly effective in warm weather, where ceiling fans can reduce the need for air conditioning.
- Reversible Function: Many ceiling fans have a reversible motor function that allows the blades to spin in either direction. In the summer, the blades spin counterclockwise to push cool air downward, while in the winter, they can spin clockwise to circulate warm air that collects near the ceiling.
3. Where Are Ceiling Fans Used? (Practical Applications)
Ceiling fans are widely used in both residential and commercial spaces to improve air circulation and create a more comfortable environment. Below are some of the most common applications of ceiling fans:
Common Applications of Ceiling Fans:
- Residential Homes: Ceiling fans are commonly installed in living rooms, bedrooms, kitchens, and dining areas. They help circulate air, reduce humidity, and provide a cost-effective cooling solution during warmer months.
- Offices and Workplaces: In office settings, ceiling fans improve airflow and maintain a comfortable environment for employees, enhancing productivity and comfort.
- Commercial Spaces: Ceiling fans are used in cafes, restaurants, hotels, and stores to create a pleasant atmosphere for customers. In these environments, they help maintain air circulation without the need for expensive air conditioning.
- Outdoor Spaces: Outdoor ceiling fans are often used in patios, porches, and verandas to provide cooling and airflow in open spaces. These fans are typically weather-resistant to handle the outdoor environment.
- Industrial Settings: Larger, industrial-grade ceiling fans are used in factories, warehouses, and gymnasiums to ensure proper ventilation and maintain a comfortable temperature for workers in large spaces.
4. How to Use Ceiling Fans Safely (Safety Guidelines and Important Tips)
Using ceiling fans safely is essential to ensure their longevity and to protect your home or workspace from electrical hazards. Below are some important safety tips for using ceiling fans effectively and safely.
Safety Tips for Using Ceiling Fans:
- Proper Installation: Ensure that your ceiling fan is installed securely on a sturdy ceiling. It is advisable to hire a professional if you are not experienced with electrical installations.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the blades regularly to remove dust and debris. Dust can accumulate on the fan blades, affecting the fan’s efficiency and causing an imbalance that may damage the motor.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Ensure that the ceiling fan’s electrical circuit is not overloaded with other appliances. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for electrical load.
- Turn Off the Fan When Not in Use: To conserve energy, turn off the fan when you are not in the room or when it is not needed. Ceiling fans are most effective when used in conjunction with other cooling or heating methods.
- Check for Loose Parts: Regularly check the fan for any loose or damaged parts, such as blades or motor components. Tighten any loose screws and replace damaged parts promptly to avoid accidents.
- Safety Precautions for Children and Pets: Keep children and pets away from ceiling fans to avoid accidents. The blades spin at high speeds, and there is a risk of injury if someone is too close to the fan.
- Use the Reversible Function Wisely: Make sure to reverse the fan’s rotation during colder months to circulate warm air back down into the room, which helps save energy by reducing the need for heating.
Conclusion
Ceiling fans are an essential addition to many homes, offices, and commercial spaces, offering effective and energy-efficient cooling and air circulation. By understanding how they work, where they can be used, and following safety guidelines, you can maximize the benefits of your ceiling fan while ensuring a safe and comfortable environment. Whether you are looking to stay cool during the summer or improve air circulation in any room, ceiling fans provide a versatile and eco-friendly solution to enhance your living or working space.